Crude oil and energy resources are the lifeblood of modern societies, fueling industries, transportation, and everyday life. These resources play a pivotal role in economic development, global trade, and geopolitical dynamics. Crude oil, in particular, is a critical commodity that has a profound impact on economies and financial markets worldwide.
Crude Oil: Crude oil is a naturally occurring fossil fuel composed of hydrocarbon deposits found beneath the Earth’s surface. It is a vital source of energy and is refined into various petroleum products such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and petrochemicals.
Energy Resources: Beyond crude oil, energy resources encompass a range of natural sources used to generate power and fuel various applications. These include natural gas, coal, renewable sources like solar and wind, and nuclear energy.
Global Dependence: Modern economies heavily rely on energy resources to power industries, transportation, homes, and technology. The availability, affordability, and sustainability of energy resources are crucial for economic growth.
Energy Markets: Energy resources are traded on global markets, where supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and technological advancements influence prices. Energy markets are sensitive to factors such as geopolitical tensions, weather patterns, and regulatory changes.
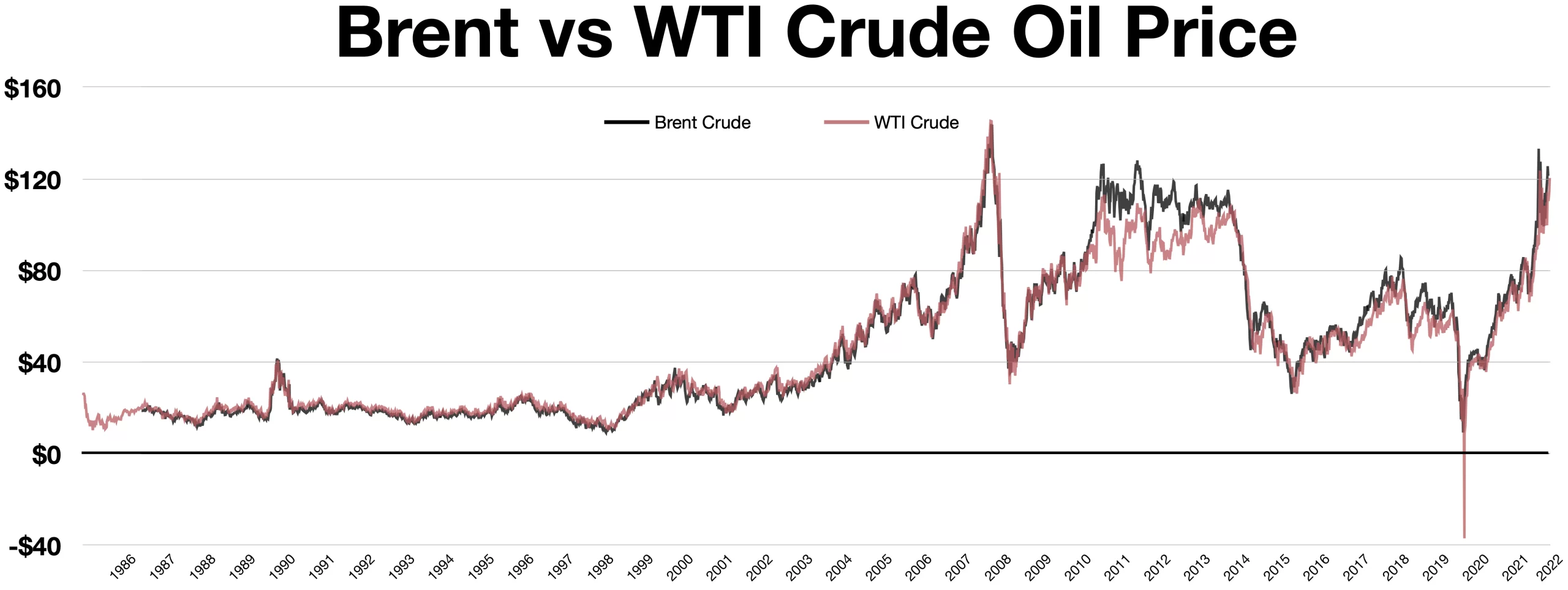
Crude Oil Grades: Crude oil comes in various grades and qualities, each with different properties that impact their refining processes and end-product yields.
Supply and Demand: The balance between global supply and demand significantly impacts energy prices. Changes in consumption patterns, economic growth, and geopolitical developments can lead to fluctuations in supply and demand dynamics.
OPEC and Non-OPEC Production: The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and non-OPEC oil-producing countries play a significant role in coordinating production levels to influence global oil prices.
Price Volatility: Energy prices, particularly crude oil prices, can experience high volatility due to factors such as geopolitical tensions, production disruptions, economic indicators, and shifts in energy policies.
Impact on Inflation: Energy prices can influence overall inflation rates, as they directly impact the cost of goods and services. Significant changes in energy prices can have broad implications for economies.
Environmental Concerns: The extraction, production, and consumption of energy resources have environmental implications. There is a growing focus on transitioning to cleaner, renewable energy sources to mitigate climate change.
Geopolitical Significance: Energy resources have geopolitical significance, often shaping international relations and conflicts. Countries with abundant energy resources can have strategic advantages in global politics.
Energy Transition: Many nations are exploring the transition to cleaner energy sources to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and address climate change concerns. This transition involves investments in renewable energy technologies and changes in energy consumption patterns.
In conclusion, crude oil and energy resources are indispensable components of modern society. They drive economies, power industries, and impact daily lives. Understanding the dynamics of energy markets, the geopolitical forces at play, and the ongoing energy transition is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers as they navigate the complex world of energy resources.